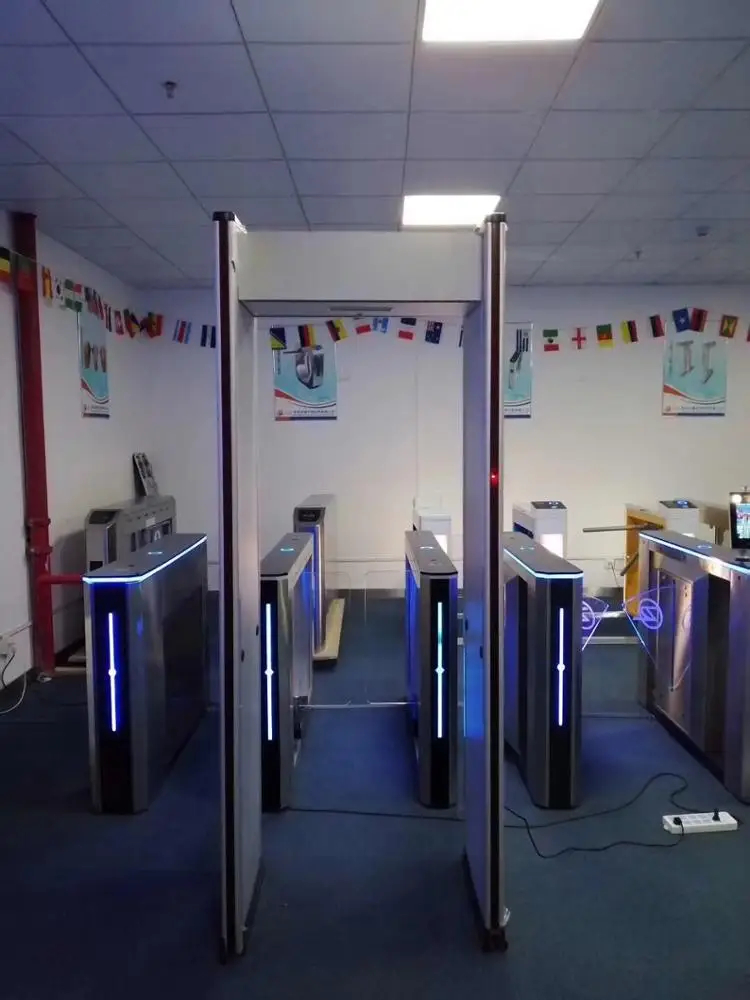
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mysteries: How Industrial Metal Detectors Work
Industrial metal detectors, a ubiquitous presence in various sectors such as food processing, mining, and security, are often viewed as enigmatic devices. However, the principles underpinning their operation are rooted in basic physics and can be comprehended with a modicum of effort. This article aims to demystify the functioning of these essential tools, thereby unlocking the secrets of industrial metal detectors.
At the heart of every industrial metal detector is the principle of electromagnetism. Essentially, these devices generate an electromagnetic field, typically by passing an electric current through a transmitter coil. When this electromagnetic field comes into contact with a metallic object, it induces electric currents, known as eddy currents, within the object. These eddy currents, in turn, generate their own magnetic field, which is detected by a receiver coil in the metal detector. The signal from the receiver coil is then processed and interpreted, alerting the operator to the presence of metal.
The sensitivity and detection range of industrial metal detectors are influenced by several factors. Firstly, the size and shape of the metallic object play a significant role. Larger and more conductive objects generate stronger eddy currents and are thus easier to detect. Secondly, the type of metal also matters. Ferrous metals, such as iron and steel, are generally easier to detect due to their high magnetic permeability, which allows them to easily generate and maintain a magnetic field. Non-ferrous metals, such as copper and aluminum, are less magnetic but are still detectable due to their ability to conduct electricity and generate eddy currents.
The operating frequency of the metal detector also plays a crucial role in its detection capabilities. Lower frequencies are more effective at detecting larger, deeper objects, while higher frequencies are better suited for detecting smaller, shallower objects. This is because lower frequencies can penetrate deeper into the ground, while higher frequencies provide greater sensitivity for small objects.
Industrial metal detectors also employ various technologies to enhance their detection capabilities. For instance, some detectors use pulse induction technology, which involves emitting a series of short, high-intensity electromagnetic pulses. This technology is particularly effective at detecting objects at greater depths and is commonly used in mining and treasure hunting. On the other hand, detectors used in food processing often use very low frequency (VLF) technology, which offers high sensitivity for small, shallow objects.
The sophistication of modern industrial metal detectors extends beyond mere detection. Advanced models are equipped with microprocessors that analyze the signal from the receiver coil to determine the type of metal detected. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as recycling, where differentiating between various types of metals is crucial.
In conclusion, the operation of industrial metal detectors, while seemingly complex, is based on the fundamental principle of electromagnetism. These devices generate an electromagnetic field, which induces eddy currents in metallic objects. The resulting magnetic field is then detected and interpreted, revealing the presence of metal. The sensitivity and detection range of these detectors are influenced by factors such as the size and type of metal, the operating frequency, and the technology employed. By understanding these principles, one can truly appreciate the ingenuity and utility of industrial metal detectors.
Unlocking the Secrets: The Role of Industrial Metal Detectors in Safety and Quality Control
Industrial metal detectors play a pivotal role in ensuring safety and quality control across a multitude of industries. These sophisticated devices, often overlooked, are the unsung heroes of the manufacturing world, tirelessly working behind the scenes to maintain the integrity of products and protect consumers. This article aims to unlock the secrets of industrial metal detectors, shedding light on their importance and functionality.
Industrial metal detectors are primarily used to detect metallic impurities within non-metallic products. They are commonly employed in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, textiles, plastics, and packaging. The primary purpose of these detectors is to identify and eliminate any metal contaminants that may have inadvertently entered the product during the manufacturing process. This is crucial as such contaminants can pose serious health risks to consumers and can also damage machinery, leading to costly repairs and downtime.
The operation of industrial metal detectors is based on the principles of electromagnetic induction. These devices generate a magnetic field, and when a metal object passes through this field, it induces an electric current. This current is detected by the device, which then triggers an alarm or stops the production line, allowing for the removal of the contaminated product. The sensitivity of the detector can be adjusted based on the size of the metal contaminants that need to be identified.
The use of industrial metal detectors is not just about safety; it’s also about maintaining quality. In the food industry, for instance, the presence of metal contaminants can significantly affect the taste, texture, and overall quality of the product. Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, metal contaminants can alter the efficacy of drugs and can even lead to serious health complications. By detecting and removing these contaminants, industrial metal detectors help ensure that the end product meets the highest standards of quality and safety.
Moreover, industrial metal detectors also play a crucial role in regulatory compliance. Many industries are subject to stringent regulations regarding product safety and quality. For instance, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States mandates that all food and pharmaceutical products be free of metal contaminants. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and even product recalls. By using industrial metal detectors, businesses can ensure that they are in full compliance with these regulations, thereby avoiding any potential legal issues.
In conclusion, industrial metal detectors are an indispensable tool in today’s manufacturing landscape. They not only ensure the safety of consumers but also help maintain the quality of products and facilitate regulatory compliance. As technology continues to advance, these devices are becoming increasingly sophisticated, capable of detecting even the smallest metal contaminants. This, in turn, is helping businesses improve their production processes, reduce waste, and deliver safer, higher-quality products to consumers. Therefore, understanding the role and functionality of industrial metal detectors is essential for anyone involved in the manufacturing industry.